- 27 Feb 2025
- 打印
- PDF
使用分割器
- 更新于 27 Feb 2025
- 打印
- PDF
注意
在 此处 下载示例程序。
在所有程序页面,点击右上角的 + New Recipe。

添加新程序弹窗将出现。输入程序的名称(必填),确保名称能反映具体应用,并从程序类型下拉菜单中选择分割。点击 OK 以创建新程序。
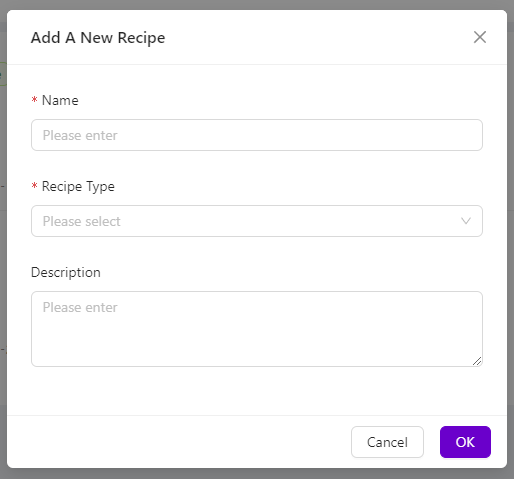
新程序将列在所有程序页面(非激活状态)。在程序右侧选择 Actions > Activate。然后点击 Activate 以确认。
点击 Edit 以开始创建您的第一个分割器模型。然后点击 Open Editor 以确认。
点击页面左下角的 Configure Imaging 开始为此应用设置您的OV20i相机。
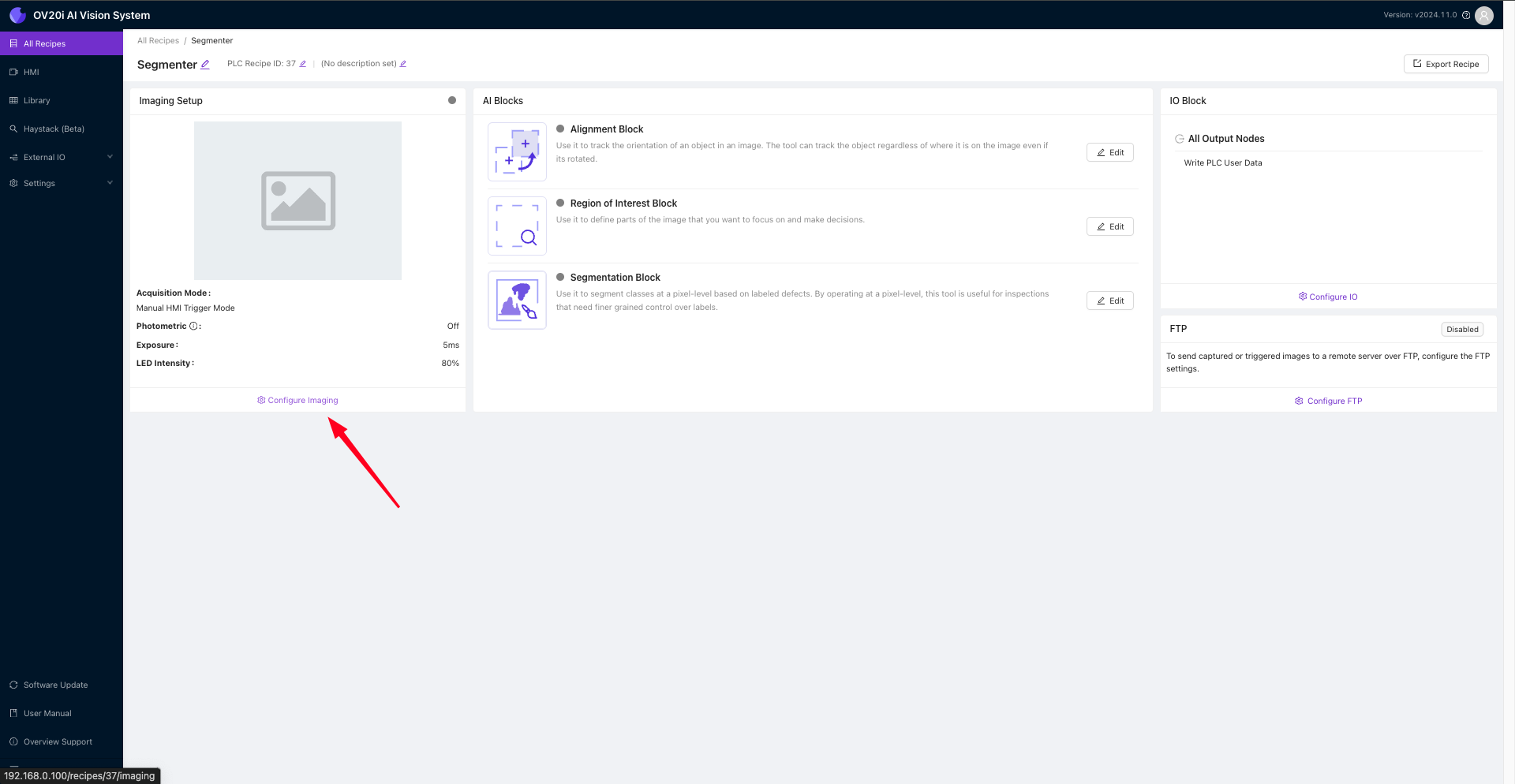
在设置相机时,务必花时间正确配置所有相机设置。这包括将相机对焦于感兴趣区域,该区域包含您要分析的物体或特征。您可以使用滑动条调整焦距,也可以手动输入数值。
另一个关键的相机设置是曝光,它控制进入相机的光线量。您可以使用滑动条调整曝光,也可以手动输入数值。
优化光照条件对于获得准确可靠的结果也至关重要。您需要确保光照条件适合您要执行的分析类型。例如,如果您正在分析反射表面,可能需要调整光照以避免眩光或反射。这可以在LED光照模式下选择。除了这些相机设置外,您还可以为相机配置内部设计的灯光,并获得不同的光照模式,以识别在不同反射条件下可能显现的缺陷。
正确设置伽马值也非常重要。伽马是衡量图像中明暗区域对比度的指标。正确调整伽马可以帮助您看到更多图像细节,并更容易识别缺陷或感兴趣的特征。
配置好所有这些设置后,只需点击 Save Imaging Settings 以应用这些设置,并开始使用相机进行分析。
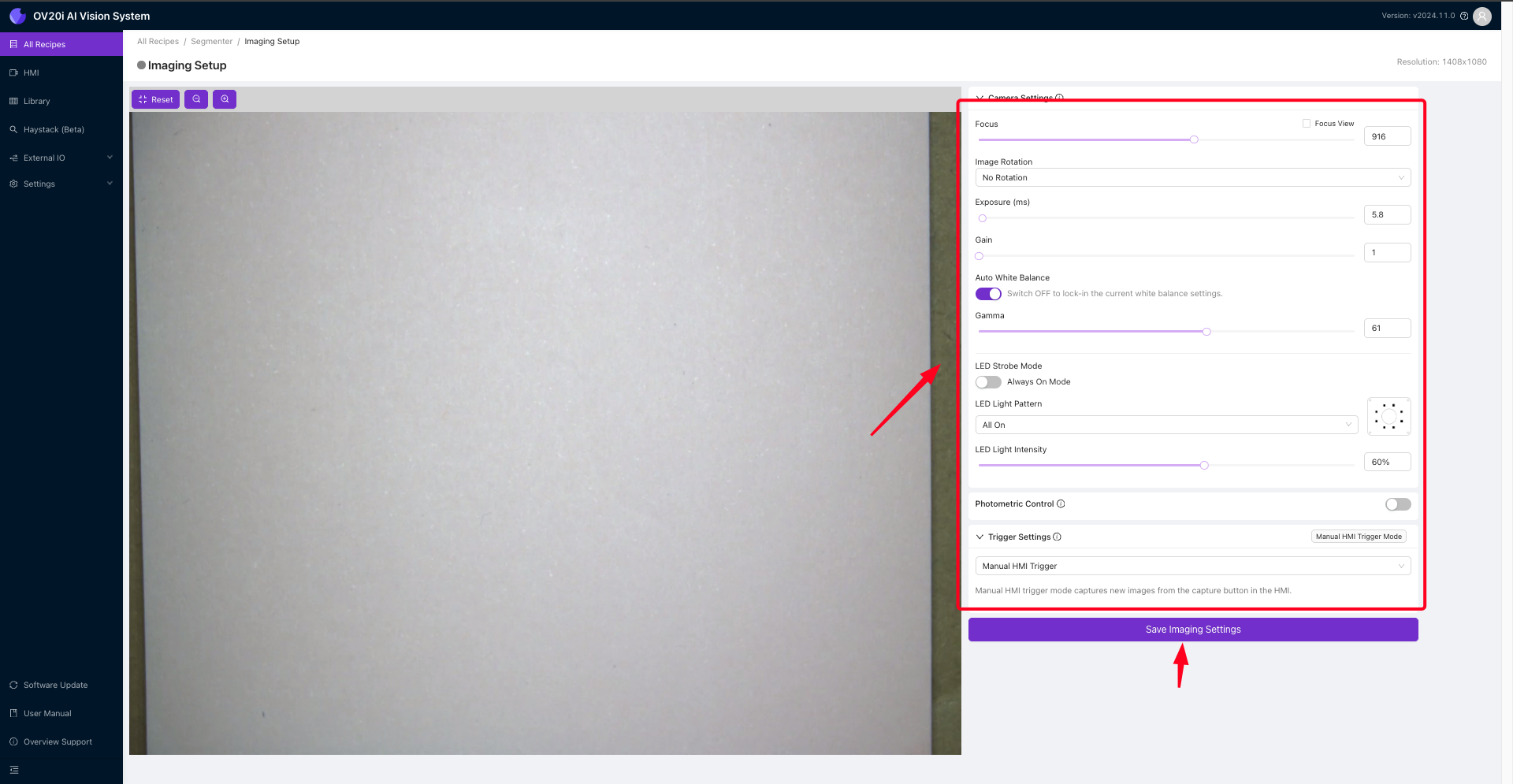
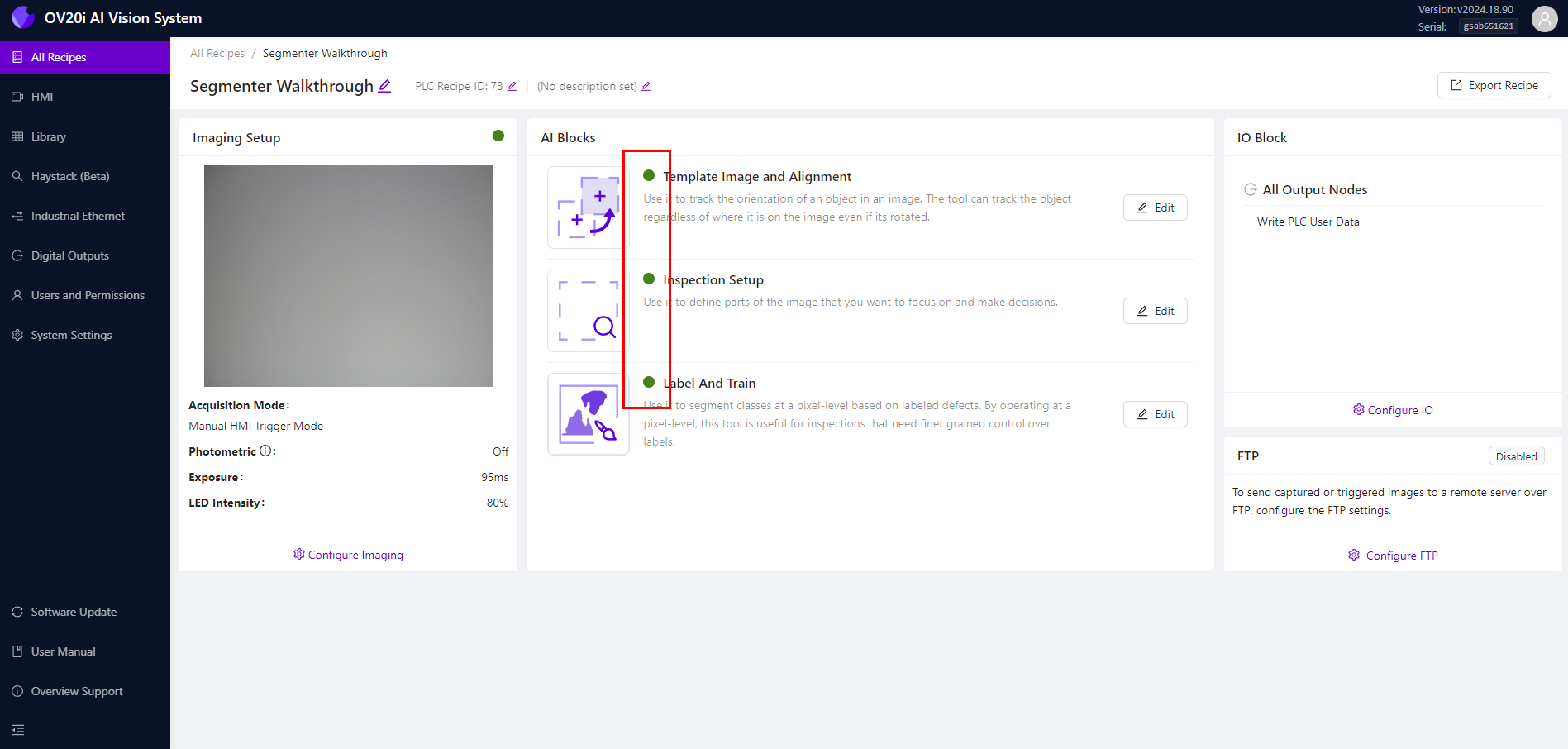
接下来,导航到 Template Image and Alignment。
导航提示
点击面包屑菜单中的程序名称以返回程序编辑器,或使用下拉菜单选择 Template Image and Alignment。
进入模板图像和对齐页面后,您可以捕捉模板图像并将页面对齐到所需状态。然而,由于当前任务不需要此步骤,请选择 Skip Aligner。完成必要的调整后,点击 Save 以应用更改并进入下一步。
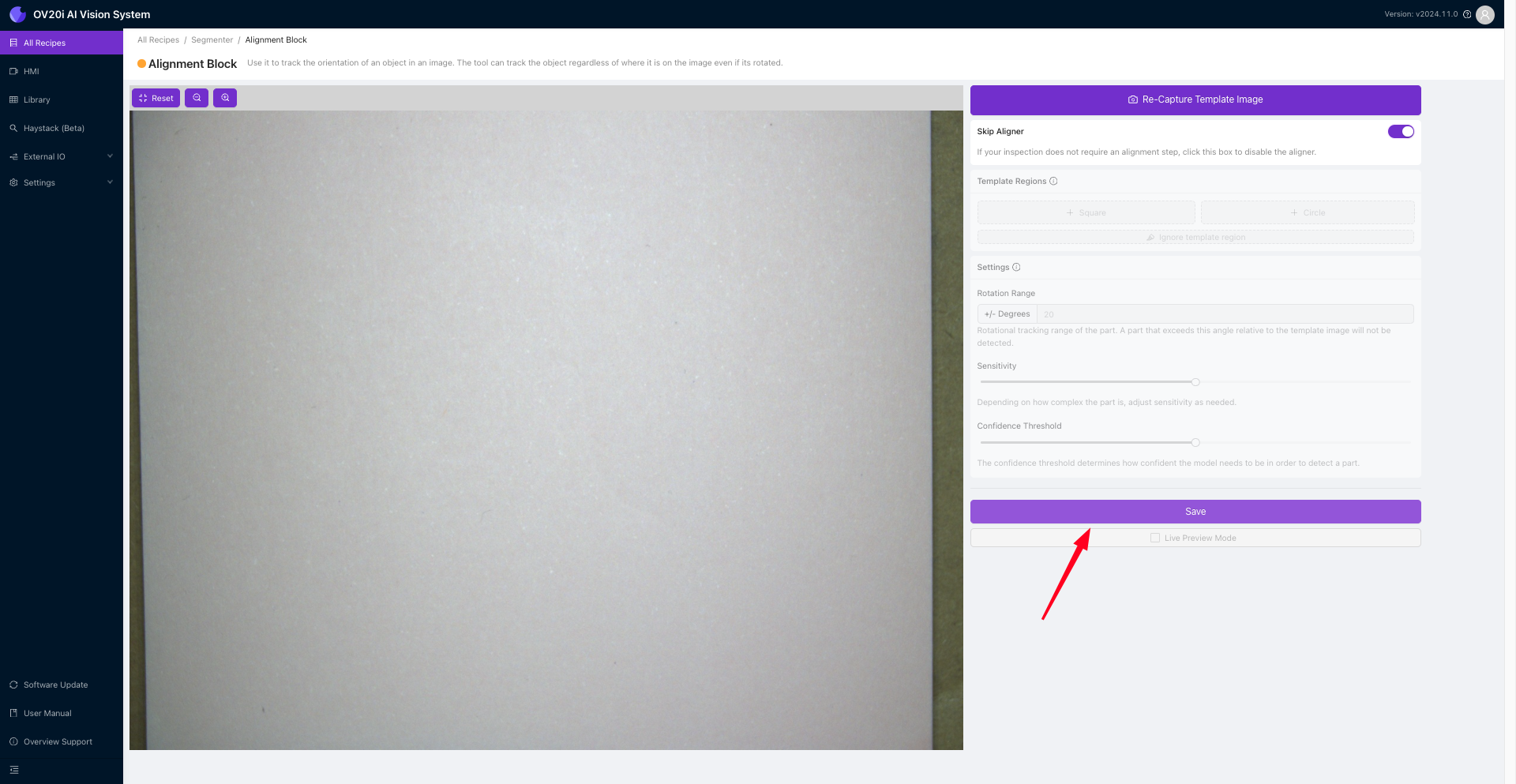
接下来,导航到 Inspection Setup。
对于这个特定情况,检测将集中在金属板上。然而,您可以根据具体应用选择不同的检测类型,并相应地调整检测区域。
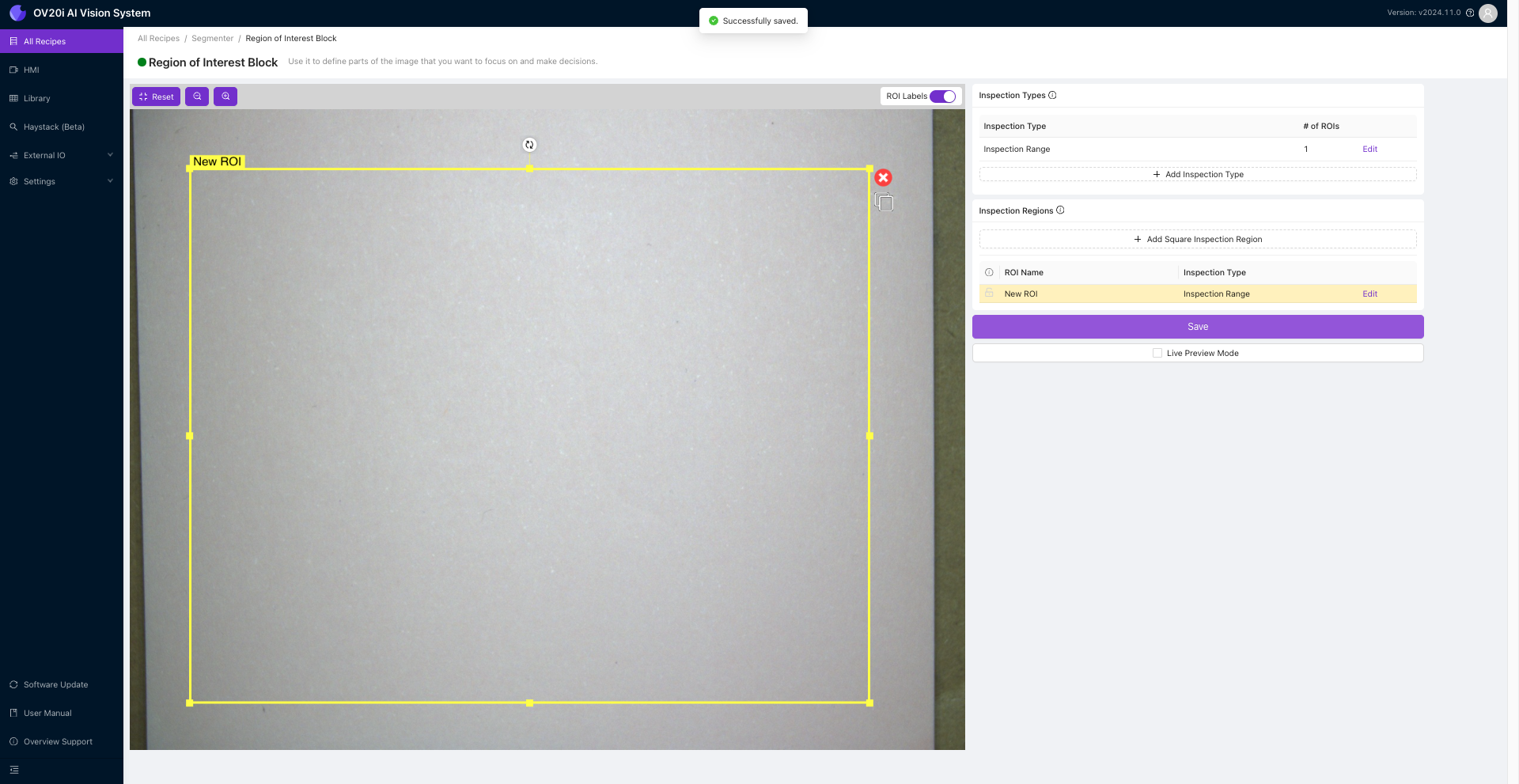
选择合适的检测类型后,您可以调整感兴趣区域(ROI),确保相机对准正确的区域。可以通过拖动ROI框的角落来调整其大小和位置。确保ROI与您要分析的物体对齐至关重要,这样才能获得最准确的结果。
调整好ROI后,只需点击 Save 以应用更改并继续检测过程。
接下来,导航到 Label And Train。
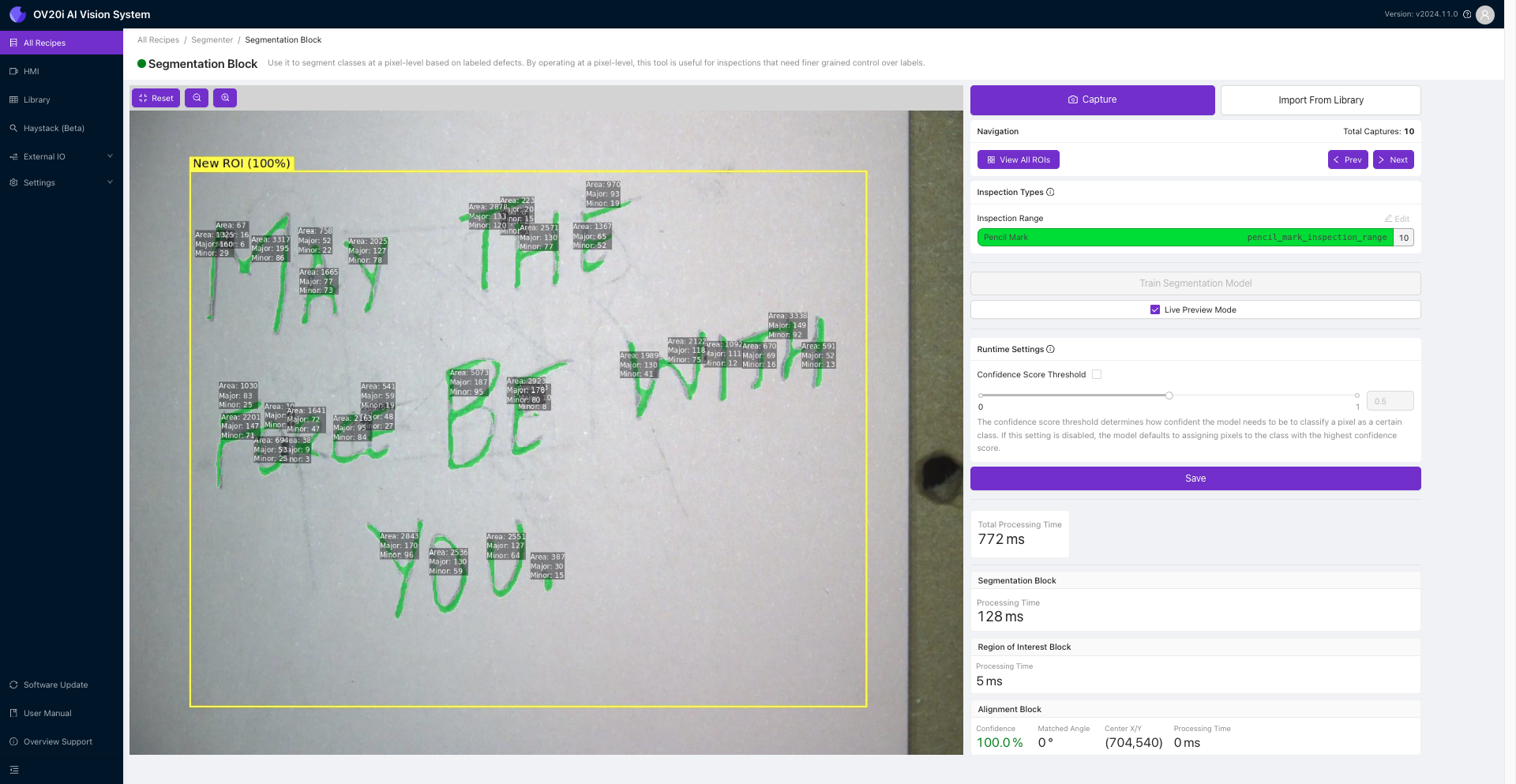
在检测类型下,点击 Edit 将类别重命名为“铅笔痕迹”。您还可以更改与该类别关联的颜色。
.png)
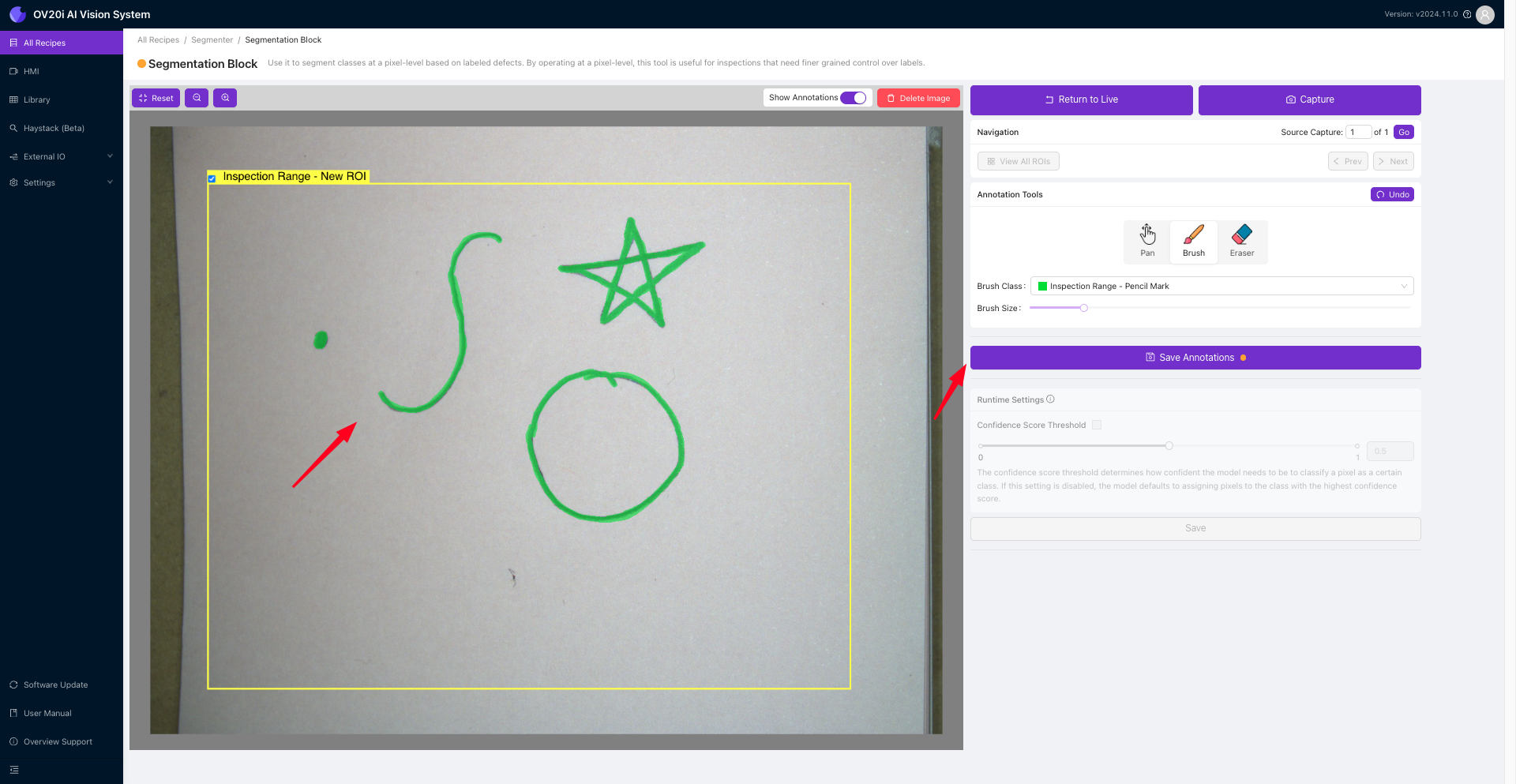
拍摄至少10张具有不同铅笔标记的金属板图像。使用 Brush 工具在每张图像中的铅笔痕迹上进行描绘。确保仅在铅笔痕迹上涂抹,不要涉及其他区域。点击 Save Annotations 并重复此过程。
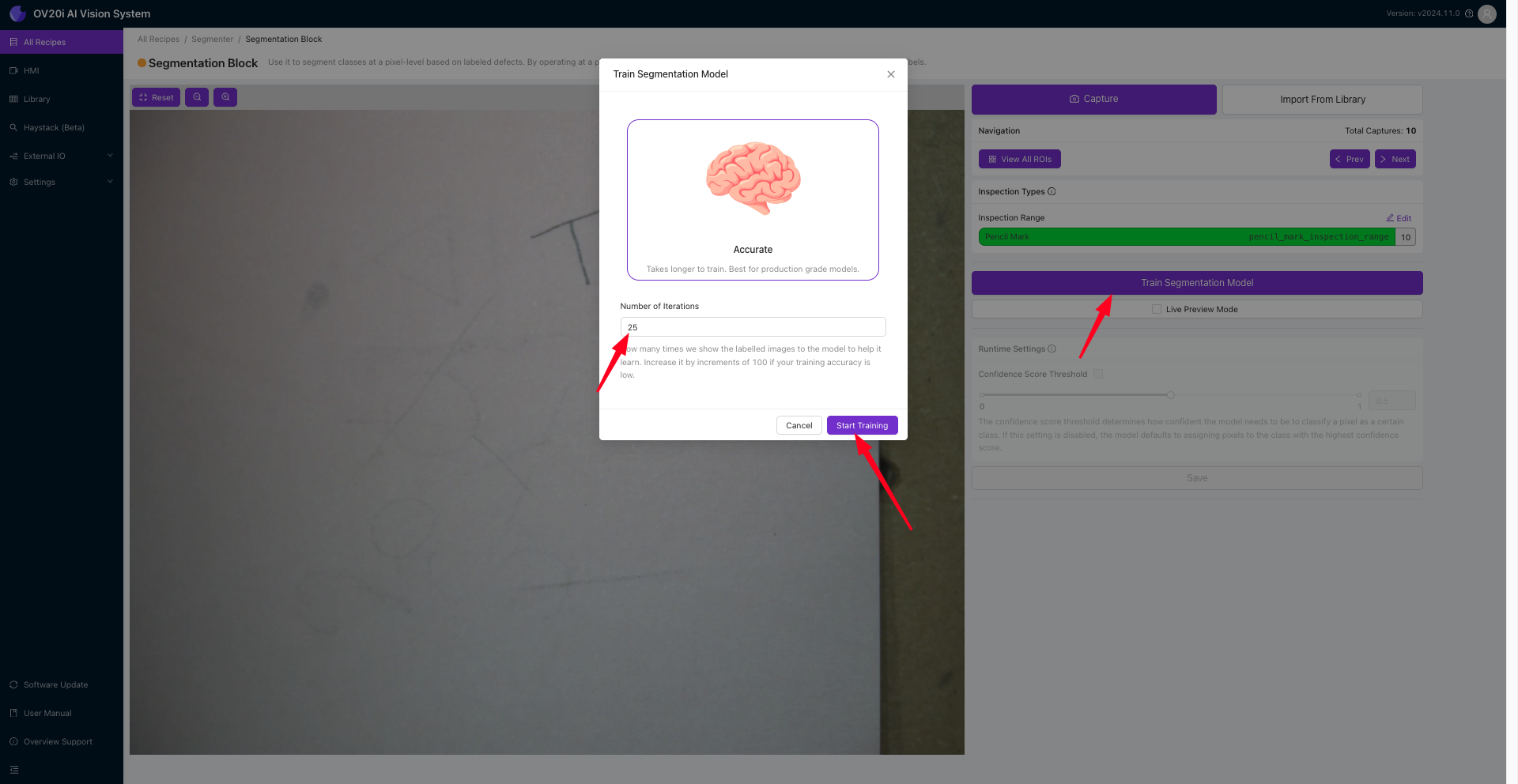
一旦标注了至少10张图像,务必仔细检查,确保所有标注都正确。验证无误后,点击 Return to Live 然后点击 Train Segmentation Model。输入您希望展示给模型的迭代次数。请记住,选择展示给模型的迭代次数越多,模型的准确性就越高。然而,更多的迭代次数将需要更长时间来训练模型。
在训练模型时,重要的是平衡准确性需求与可用的训练时间。一旦选择了合适的设置,点击 Start Training 按钮以启动训练过程。系统将开始训练模型,您可以监控其进度,并根据需要进行调整。
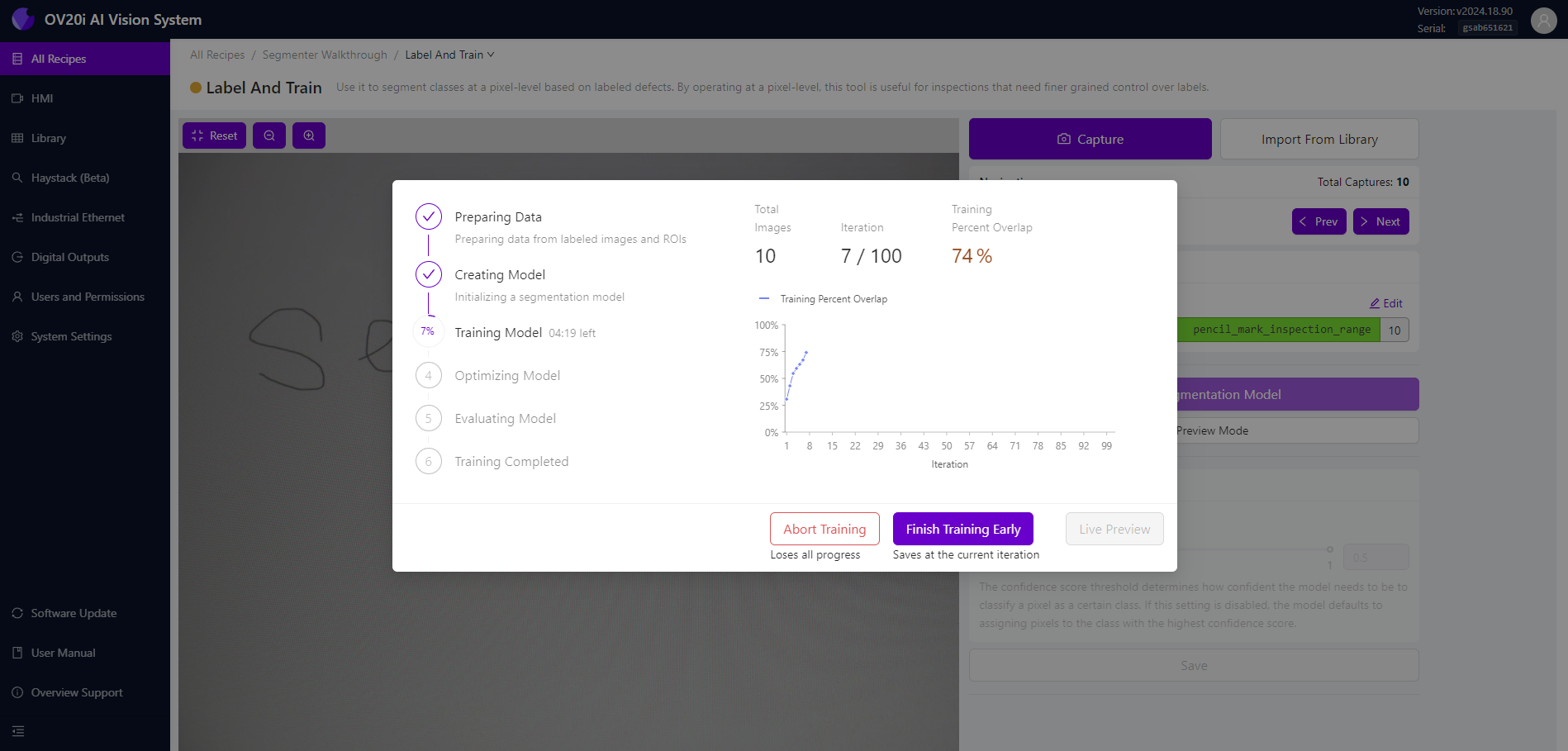
点击 Start Training 按钮后,将显示模型训练进度弹窗。在此,您可以查看当前的迭代次数和准确率值。如果需要因任何原因停止训练,请点击 Abort Training 按钮。如果训练准确率已经足够,您可以通过点击 Finish Training Early 按钮来提前完成训练。
注意
如果训练准确率达到预定标准,训练将自动完成。
训练完成后,您可以检查训练准确率并评估模型在验证数据上的表现。如果您对结果满意,可以保存模型并用于分析。如果不满意,您可以返回调整设置并重新训练模型,直到对模型性能感到满意为止。
训练完成后,点击 Live Preview 查看训练模型的实时预览,突出显示铅笔痕迹。恭喜!您已成功训练了第一个分割模型。
配置合格/不合格逻辑
在以下步骤中,我们将指导您如何使用Node-RED逻辑为分割程序配置合格/不合格逻辑。
注意
在编辑IO块之前,请确保所有AI块已训练完成(绿色)。
通过面包屑菜单导航到IO块,或在程序编辑器页面选择 Configure I/O。

删除分类块逻辑,然后通过从左侧拖动节点并将它们连接起来,构建以下Node-RED流程。
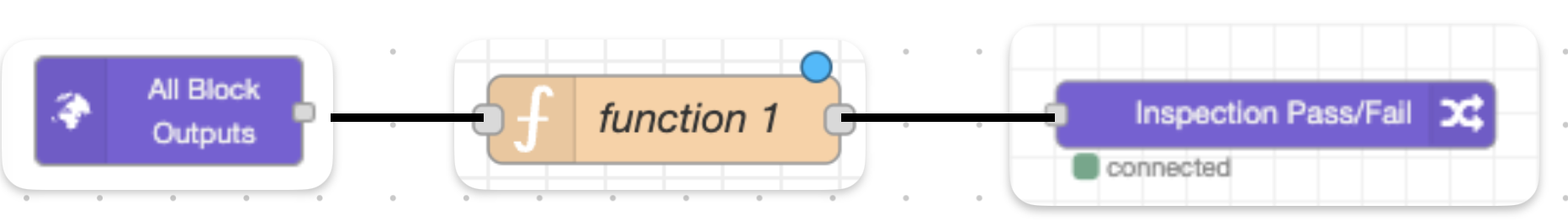
双击 function 1 然后将以下部分中的示例代码复制并粘贴到 On Message 标签页中。
.png)
点击 Done。
点击 Deploy。
导航到HMI并测试您的逻辑。
代码示例
如果未检测到像素,则通过
复制并粘贴以下逻辑:
const allBlobs = msg.payload.segmentation.blobs; // 从有效负载的分割数据中提取斑点信息
const results = allBlobs.length < 1; // 检查是否没有斑点,并存储结果(true 或 false)
msg.payload = results; // 将有效负载设置为检查结果
return msg; // 返回修改后的消息对象如果检测到的所有斑点均小于设定阈值,则通过
复制并粘贴以下逻辑:
const threshold = 500; // 定义像素计数的阈值
const allBlobs = msg.payload.segmentation.blobs; // 从有效负载的分割数据中提取斑点信息
const allUnderThreshold = allBlobs.every(blob => blob.pixel_count < threshold); // 检查所有斑点的像素数是否小于阈值
msg.payload = allUnderThreshold; // 将有效载荷设置为检查结果
return msg; // 返回修改后的消息对象如果检测到的像素总数小于设定阈值,则通过
复制并粘贴以下逻辑:
const threshold = 5000; // 定义像素计数的阈值
const allBlobs = msg.payload.segmentation.blobs; // 从有效负载的分割数据中提取斑点信息
const totalArea = allBlobs.reduce((sum, blob) => sum + blob.pixel_count, 0); // 计算所有斑点的总像素数
msg.payload = totalArea < threshold; // 如果总面积小于阈值,则将有效载荷设置为 true,否则设置为 false
return msg; // 返回修改后的消息对象